
and Nederhof, M.-J.: A modular proof of strong normalization for the calculus of constructions, J. Thesis, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Nijmegen, 1993. Geuvers, H.: Logics and Type Systems, Ph.D. Gentzen, G.: The Collected Papers of Gerhard Gentzen, Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics, North-Holland, 1969. Odifreddi (ed.), Logic and Computer Science, APIC Studies in Data Processing 31, Academic Press, 1990, pp. Gallier, J.: On Girard' “ Candidats de reductibilit é, in P. and Pitts, A.: A new approach to abstract syntax involving binders, in G. Geuvers (ed.), Informal Proceedings of the Nijmegen Workshop on Types for Proofs and Programs, 1993.įeferman, S.: Finitary inductively presented logics, in ' 88, Padova, North-Holland, 1988. and Boyer, R.: Towards checking proof checkers, in H. Plotkin (eds.), Logical Frameworks, 1991.Ĭoquand, T.: An algorithm for type-checking dependent types, Sci. Ĭoquand, T.: An algorithm for testing conversion in type theory, in G. Thesis, Dipartimento di Informatica, Torino, Italy, 1990.Ĭardelli, L.: F-sub, the system, Technical report, DEC Systems Research Centre, 1991.Ĭoquand, C.: Combinator shared reduction and infinite objects in type theory, 1996. 34-57.īerardi, S.: Type Dependence and Constructive Mathematics, Ph.D. P.-A.: On the subject reduction property for algebraic type systems, in CSL'96: Proceedings of the 10th Annual Conference of the European Association for Computer Science Logic, Utrecht, LNCS 1258, 1997, pp.

et al.: The Coq proof assistant reference manual, INRIA-Rocquencourt, 1998.īarras, B.: Coq en Coq, Rapport de Recherche 3026, INRIA, 1996.īarthe, G.

II, Oxford University Press, 1992.īarras, B. t \lambda x.Altenkirch, T.: A formalization of the strong normalization proof for System F in LEGO, in Proceedings of the International Conference on Typed Lambda Calculi and Applications, TLCA'93, LNCS 664, 1993.īarendregt, H.: Lambda calculi with types, in Abramsky, Gabbai, and Maibaum (eds.), Handbook of Logic in Computer Science, Vol. See §Notation, below for when to include parenthesesĪn abstraction λ x. For example, the outermost parentheses are usually not written. However, some parentheses can be omitted according to certain rules. Thus a lambda term is valid if and only if it can be obtained by repeated application of these three rules. M ) is a lambda term (called an application). x x : Some lambda term, a character or string representing a parameter, or mathematical/logical value.
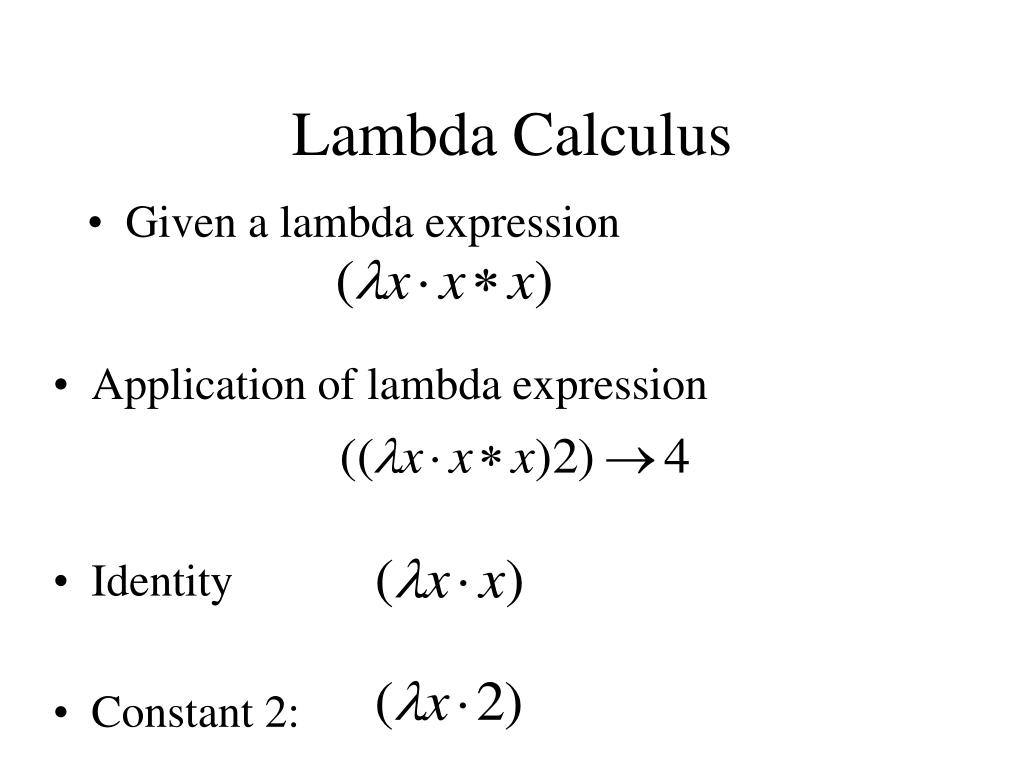
In the simplest form of lambda calculus, terms are built using only the following rules:

Lambda calculus consists of constructing lambda terms and performing reduction operations on them. It was introduced by the mathematician Alonzo Church in the 1930s as part of his research into the foundations of mathematics. It is a universal model of computation that can be used to simulate any Turing machine. Lambda calculus (also written as λ-calculus) is a formal system in mathematical logic for expressing computation based on function abstraction and application using variable binding and substitution. Mathematical-logic system based on functions


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
